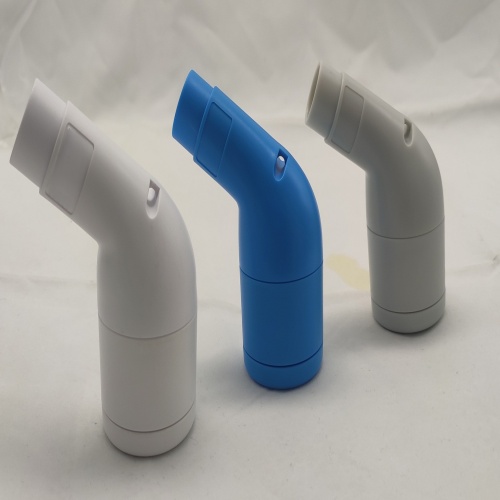
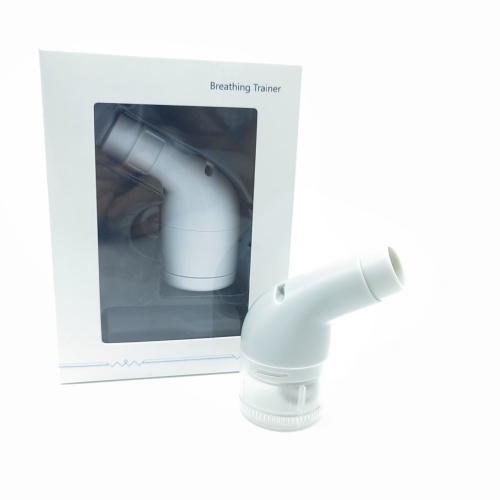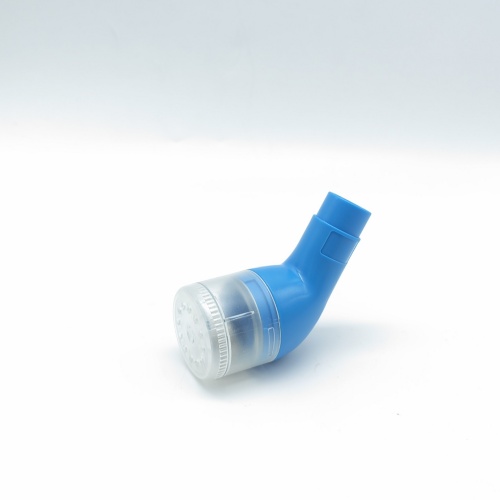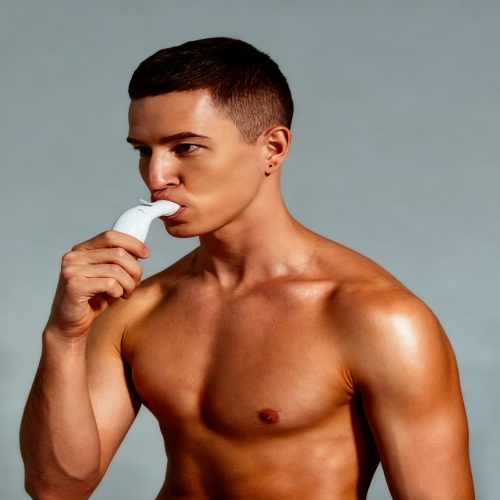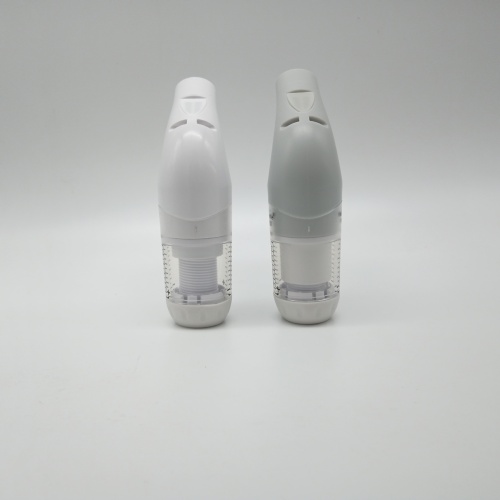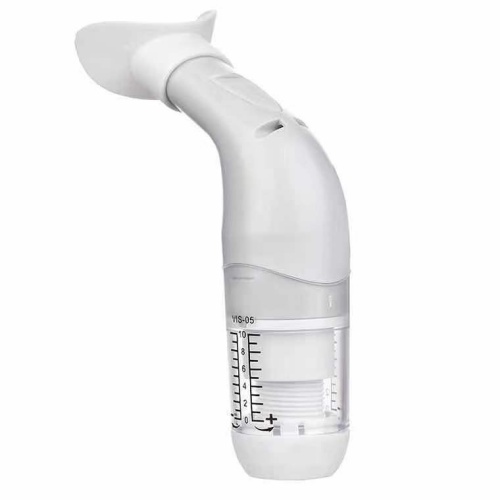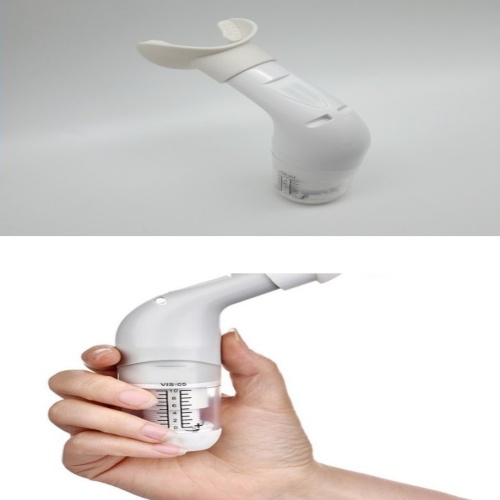
Portable lung function deep breathing trainer
Portable deep breathing trainers primarily provide targeted breathing exercises, with the following benefits:
Improving lung function and vital capacity: Continuous deep breathing training can effectively increase lung ventilation and alveolar exchange, thereby improving vital capacity.
Strengthening respiratory muscles: By adjusting resistance, the diaphragm, intercostal muscles, and other respiratory muscles are forced to work harder, thereby increasing their strength and endurance. Studies have shown that continuous training can improve respiratory muscle strength by an average of 20%-30%.
Assisting with expectoration and preventing complications: Models with a positive oscillatory pressure (PEP) function, in particular, generate vibrations and positive pressure during exhalation to help loosen and clear phlegm deep in the airways. This is particularly important for patients recovering from surgery and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Preventing atelectasis: After thoracic and abdominal surgery, encouraging patients to breathe deeply helps expand the alveoli and prevent atelectasis (lung collapse).
Suitable for: Postoperative recovery: Particularly suitable for patients recovering from cardiac, thoracic, and abdominal surgery, it can effectively prevent lung infections and atelectasis.
Patients with respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma can use it for daily rehabilitation exercises to slow lung function decline and improve breathing difficulties.
Long-term smokers and the elderly can use it to help improve lung function decline caused by smoking or aging.
Athletes, such as long-distance runners and swimmers, can improve their oxygen uptake and breathing efficiency through training.
Common breathing trainers on the market are based on the following principles:
Resistance training: The user is required to breathe harder against a set resistance set by the breathing trainer, thereby strengthening the respiratory muscles.
Visual feedback: For example, the classic three-ball breathing trainer, with the balls rising during inhalation, provides a clear goal and visual motivation.
Positive end-expiratory pressure with vibration: This combines positive end-expiratory pressure (PEP) with low-frequency oscillation technology to help open the airways during exhalation and vibrate sputum, making exhalation easier.
Suitable for:
Thoracoabdominal surgery patients recovering from surgery
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, and other respiratory diseases
Long-term smokers and elderly individuals with deteriorating lung function
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts